Creating and Querying Data in MySQL Database
12002Introduction to This Lesson
In this lesson, we will learn the basic structure of MySQL databases, including the relationship between databases and data tables, as well as the concept of data tables. By understanding these concepts, we will learn how to use SQL statements to create databases and data tables, understand their structure, and learn how to use basic SQL query statements like SELECT to query data.
1. Understanding the Structure of MySQL Database
Structure of MySQL Database
In Lesson 01, we introduced the concept of relational databases. MySQL is a relational database that stores data in tabular form, where each table is referred to as a data table. There can be different types of relationships between data tables in a database, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many. These relationships define how data is connected and interacted with, helping us better organize and manage data.
Structure of Data Tables
- Understanding Data Tables
A data table is a fundamental object in a relational database, similar to a folder in a filing cabinet, storing a specific type of data. For example, a "Customer Table" that records customer information may include basic information such as customer name, address, and phone number.
- Structure of Data Tables
Data tables consist of multiple "rows" and "columns," similar to an Excel spreadsheet, where each row represents a record of data and each column represents a type of data.
Thus, in a data table, each column has a name (field name) that defines the type of data in that column (such as integer, string, date, etc.). Each row contains specific values for each field in the table, and these values constitute a complete data record.
Relationship Between Databases and Data Tables
To use a metaphor, a database is like a folder, while data tables are like files within that folder. We manage tables through the database to achieve data storage and management. The relationship between databases and data tables can be summarized as follows:
Database as a Container for Tables: In a relational database, a database is a container for storing tables. A database can contain one or more tables, and each table has a unique name used to identify it within the database.
Tables as Structured Representations of Data: Tables are the basic storage units of data in a relational database. Each table consists of rows and columns. Rows represent data records, while columns define the types and names of the data. For example, a "Student" table may contain columns such as "Student ID," "Name," and "Age."
Database Provides Management Functions for Tables: A database is not just a container for tables; it also provides management functions for them. For example, you can create, delete, modify tables, or query data within tables in the database. The database also provides mechanisms for data integrity and security, such as transaction management and access control.
Tables Can Be Related: Within the same database, tables can be connected through relationships. This is an important feature of relational databases. For example, the "Student" table and the "Course" table can be linked through an "Enrollment" table, indicating which student is enrolled in which course.
Now that we understand the structure of databases, the structure of data tables, and the relationship between databases and data tables, we can proceed to create databases and data tables, further understanding the concepts through practice.
2. Creating Databases and Data Tables
The simplest way to create databases and data tables is to use SQL statements. Below, we will provide a simple example to teach you how to create databases and data tables using SQL statements in Navicat, further understanding the appearance and structure of databases and data tables through practice.
Creating a Database Using SQL Statements
- Select the MySQL database connection you want to open, right-click, and choose "Open Connection."
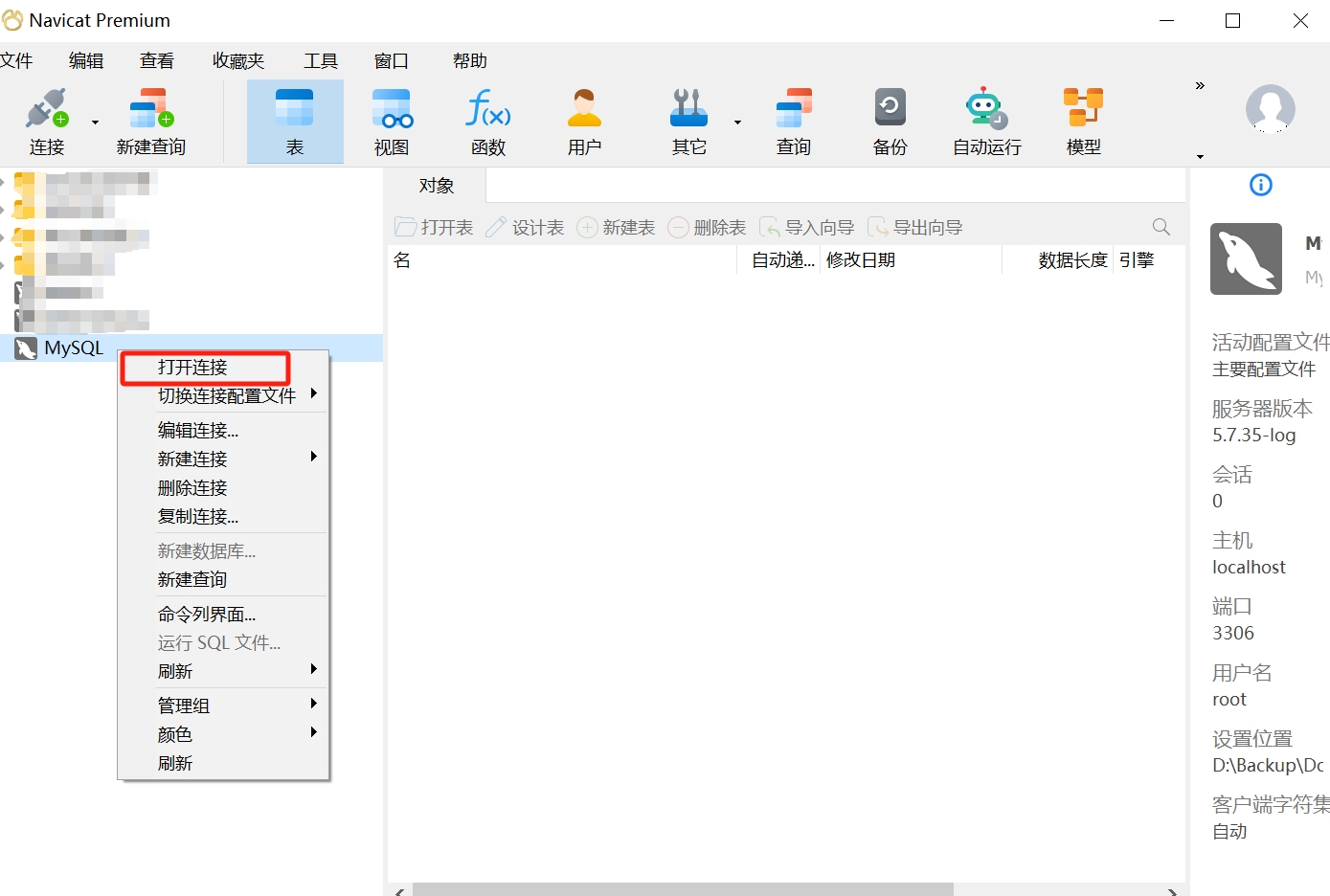
- After opening the connection, click "New Query" in the navigation bar.
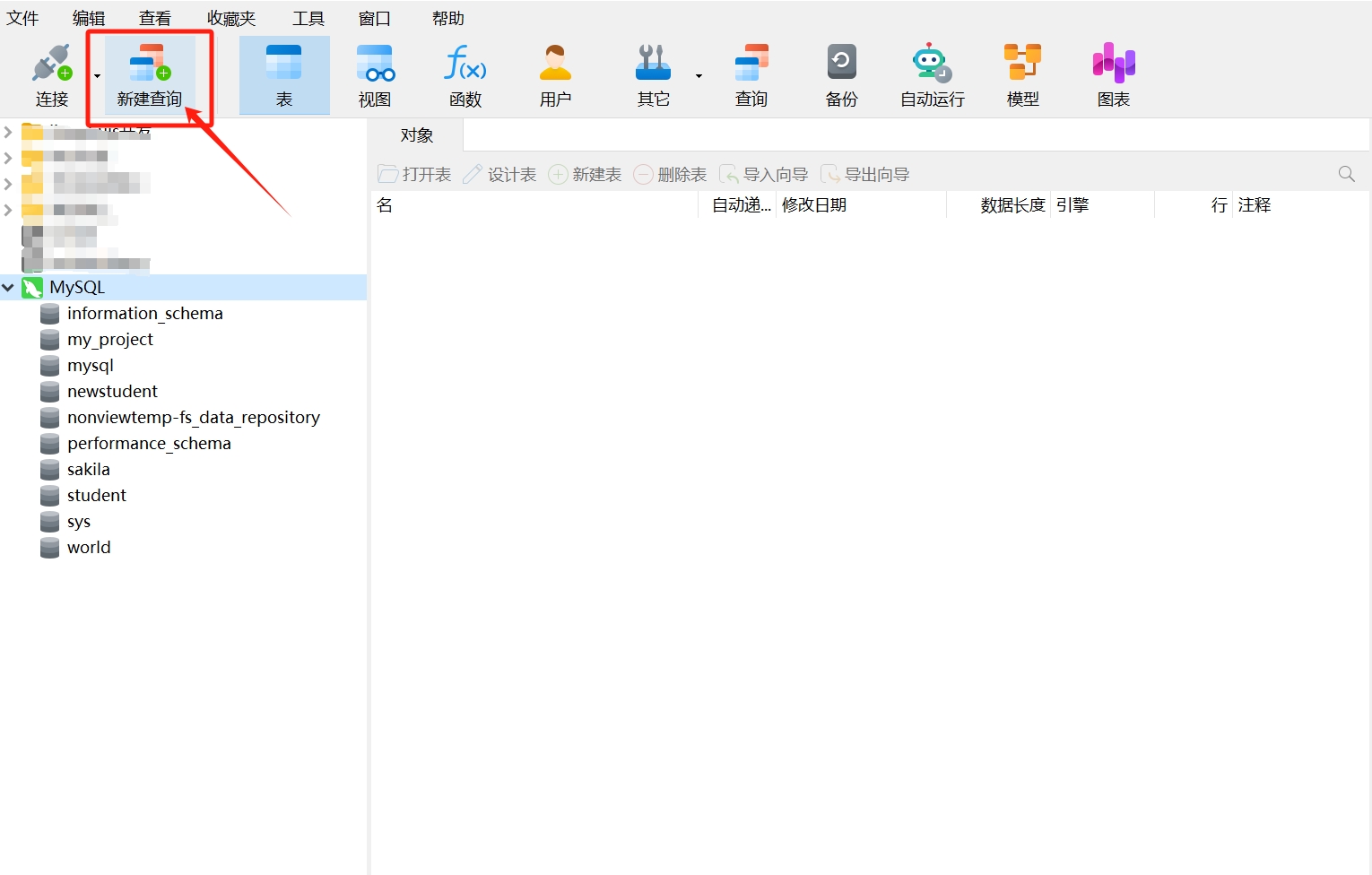
- After clicking, an SQL editor will appear. Note: Ensure that the database connection name displayed in the editor matches the name of the database connection you opened to avoid creating the new database in another connection.
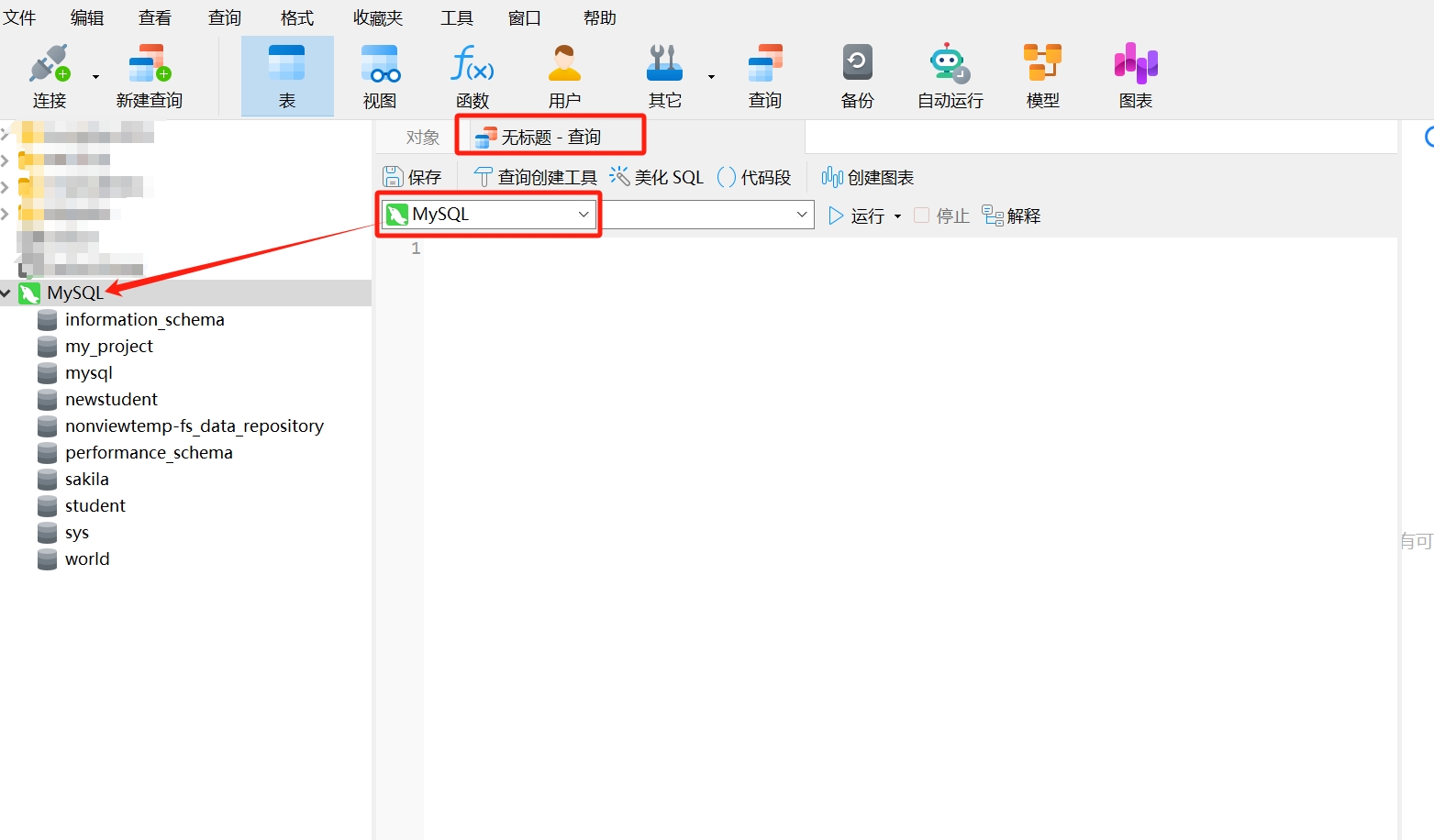
- Copy the following SQL statement to create a new database and paste it into the opened query window, where "mystudent" is the name of the new database, then click "Run."
CREATE DATABASE mystudent;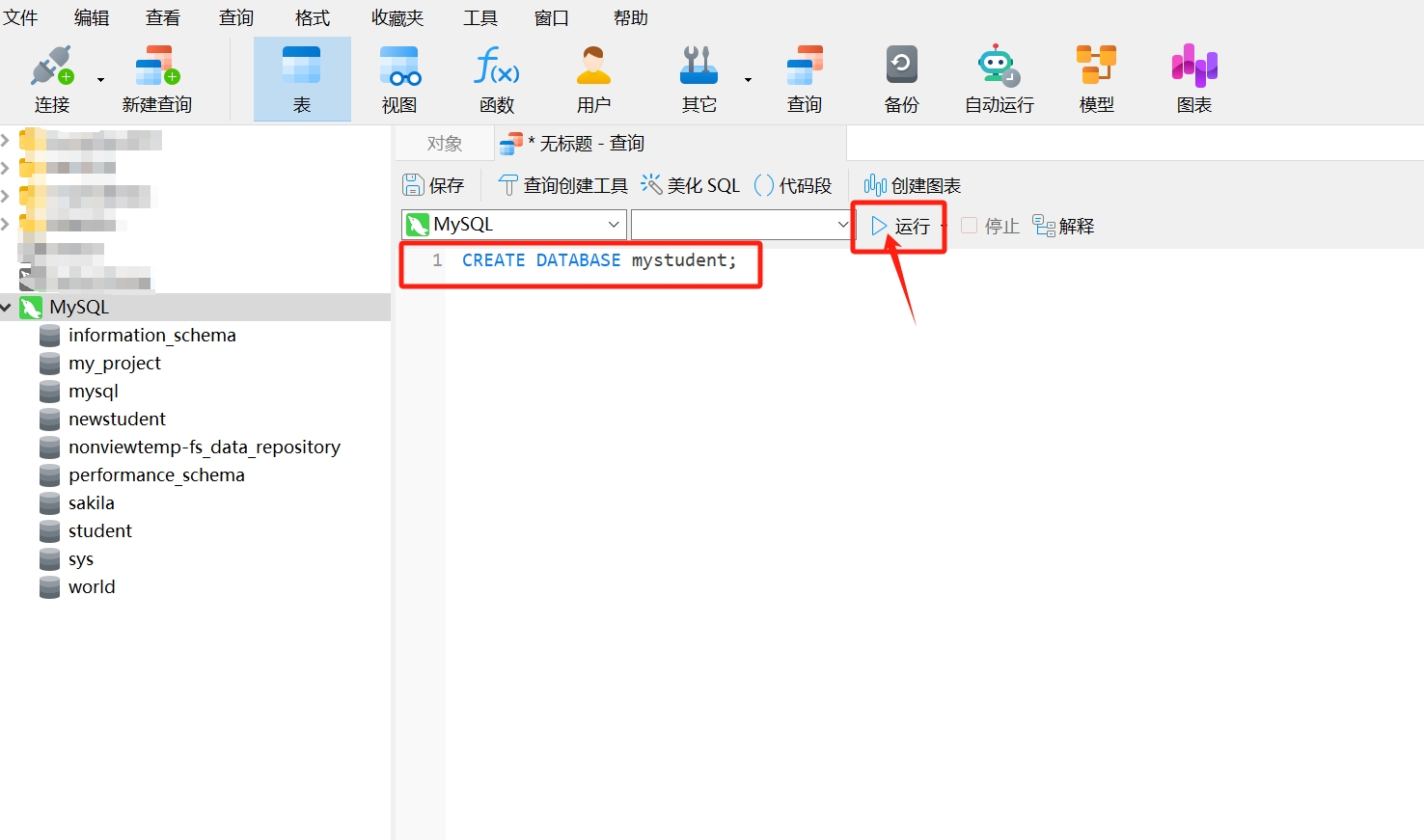
- After running, you will see a query result as follows; the information bar displays "OK," indicating that the database "mystudent" has been created.
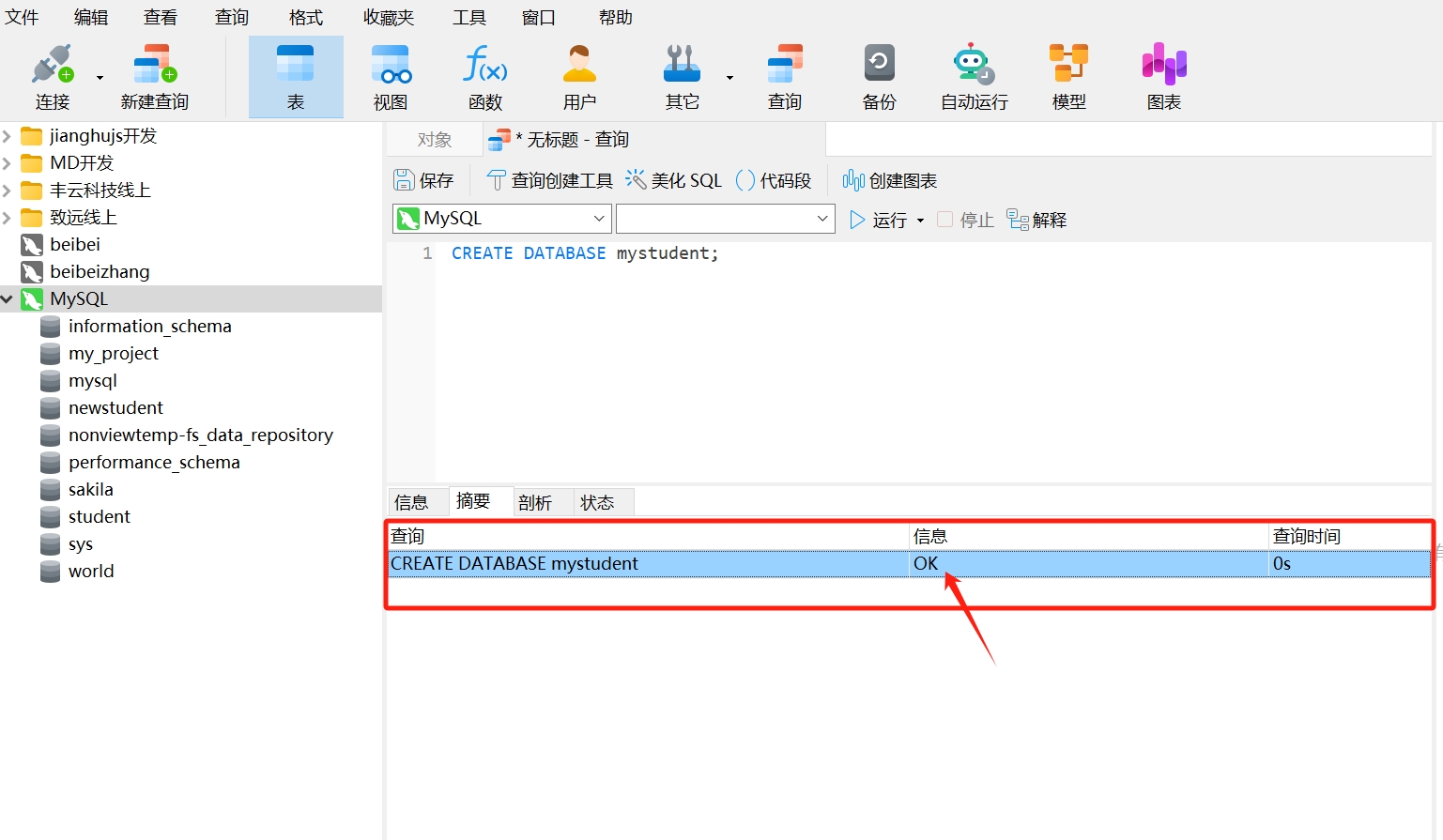
- Right-click and select "Refresh."
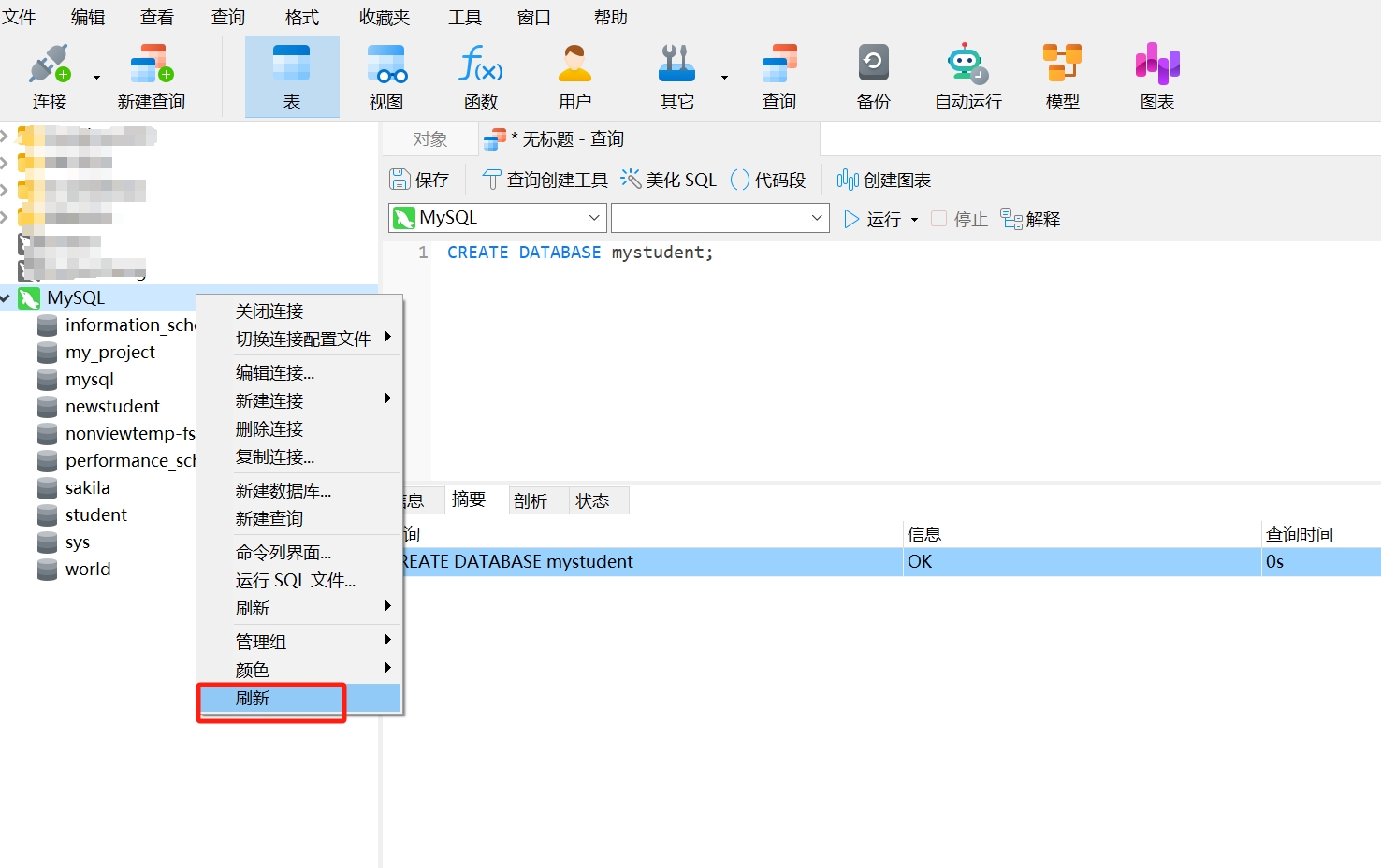
- After refreshing, the created database "mystudent" will appear in the MySQL connection. Double-click "mystudent" to open the database.
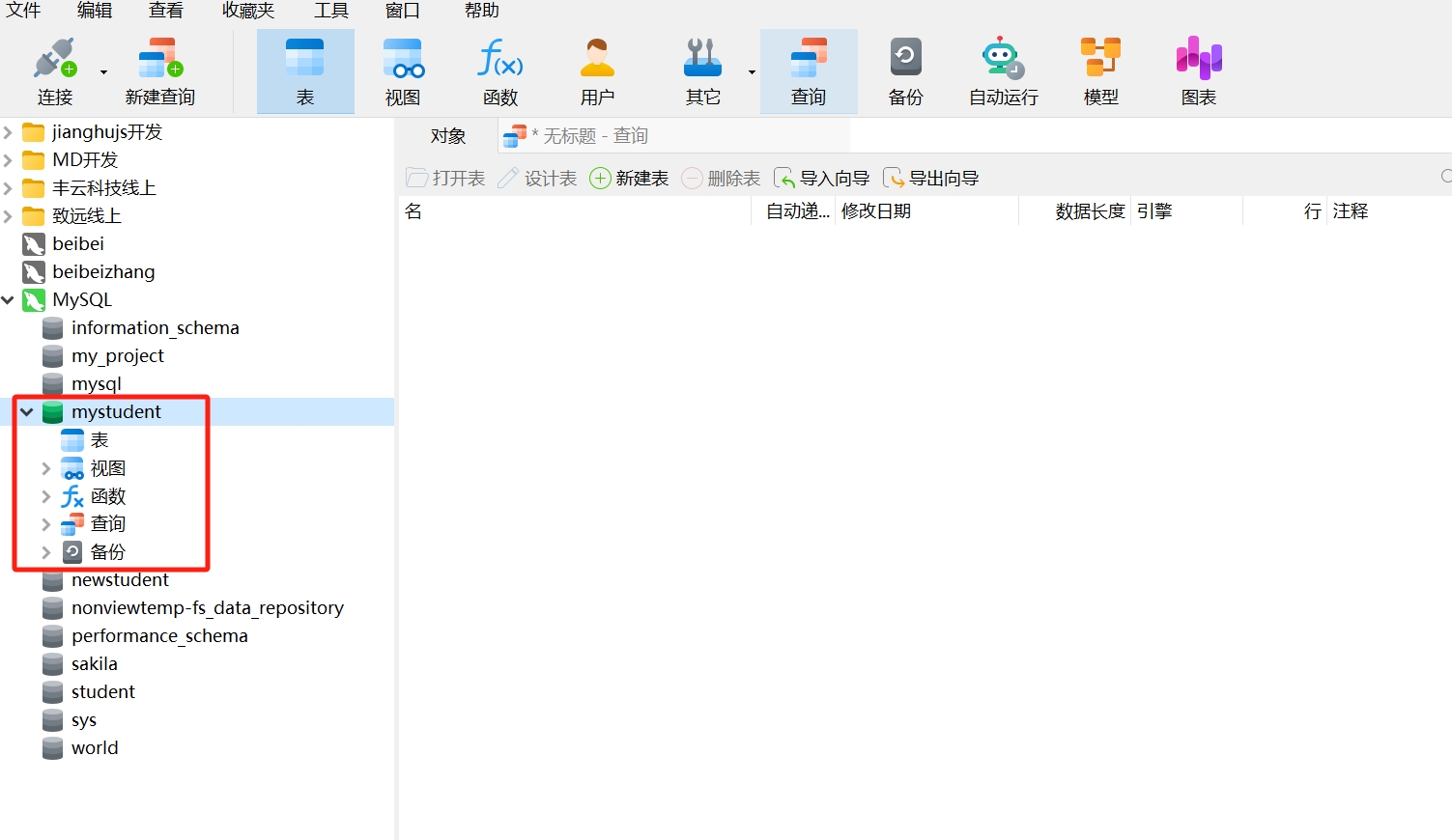
Creating a database is very simple. The created database includes tables, views, functions, queries, and backups, which are all important components and common functions of a database. Next, we will continue to create data tables in the newly created "mystudent" database.
Creating a Data Table Using SQL Statements
- After selecting the database "mystudent," click "New Query" in the navigation bar. You will see that the database connection name and database name in the SQL editor match the names of the selected data connection and database.
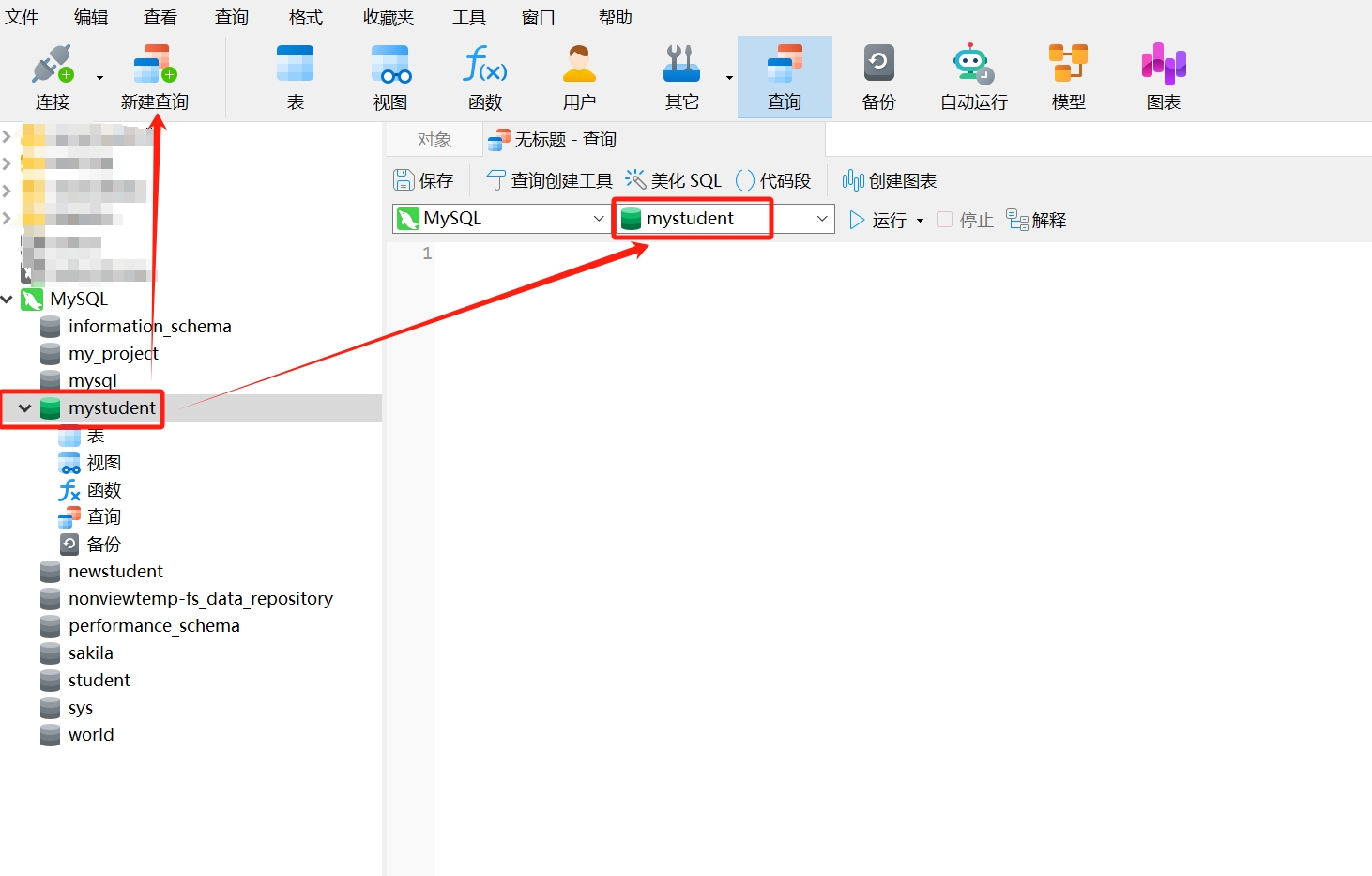
- Copy the following SQL statement to create a new data table and paste it into the opened query window, where "student" is the name of the new data table, and "id," "studentId," "name," and "gender" are the column names of the data table, then click "Run."
CREATE TABLE student (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
studentId VARCHAR(255),
name VARCHAR(255),
gender VARCHAR(255),
age INT
);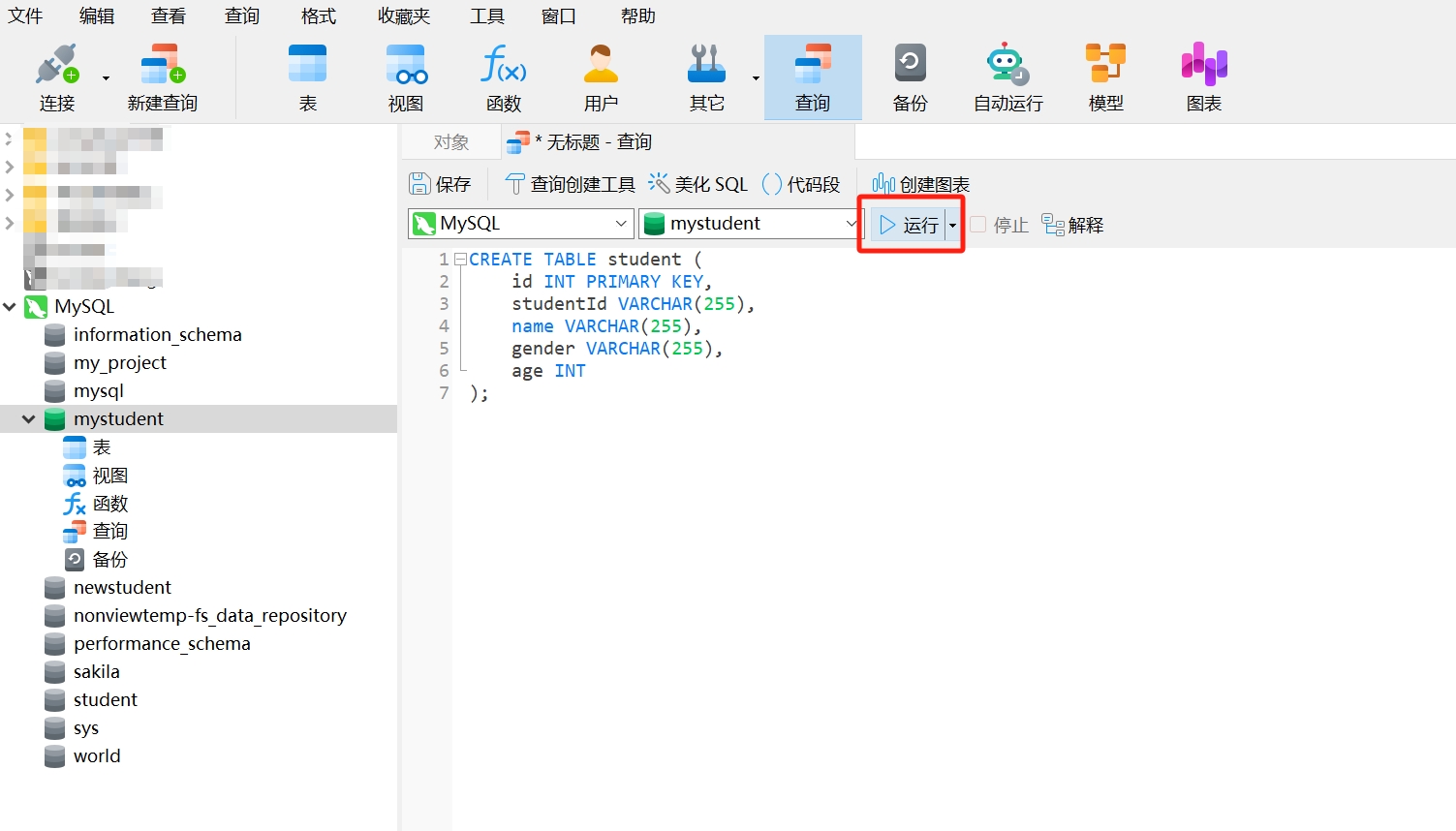
- After running, you will see a query result as follows; the information bar displays "OK," indicating that the data table "student" has been created.
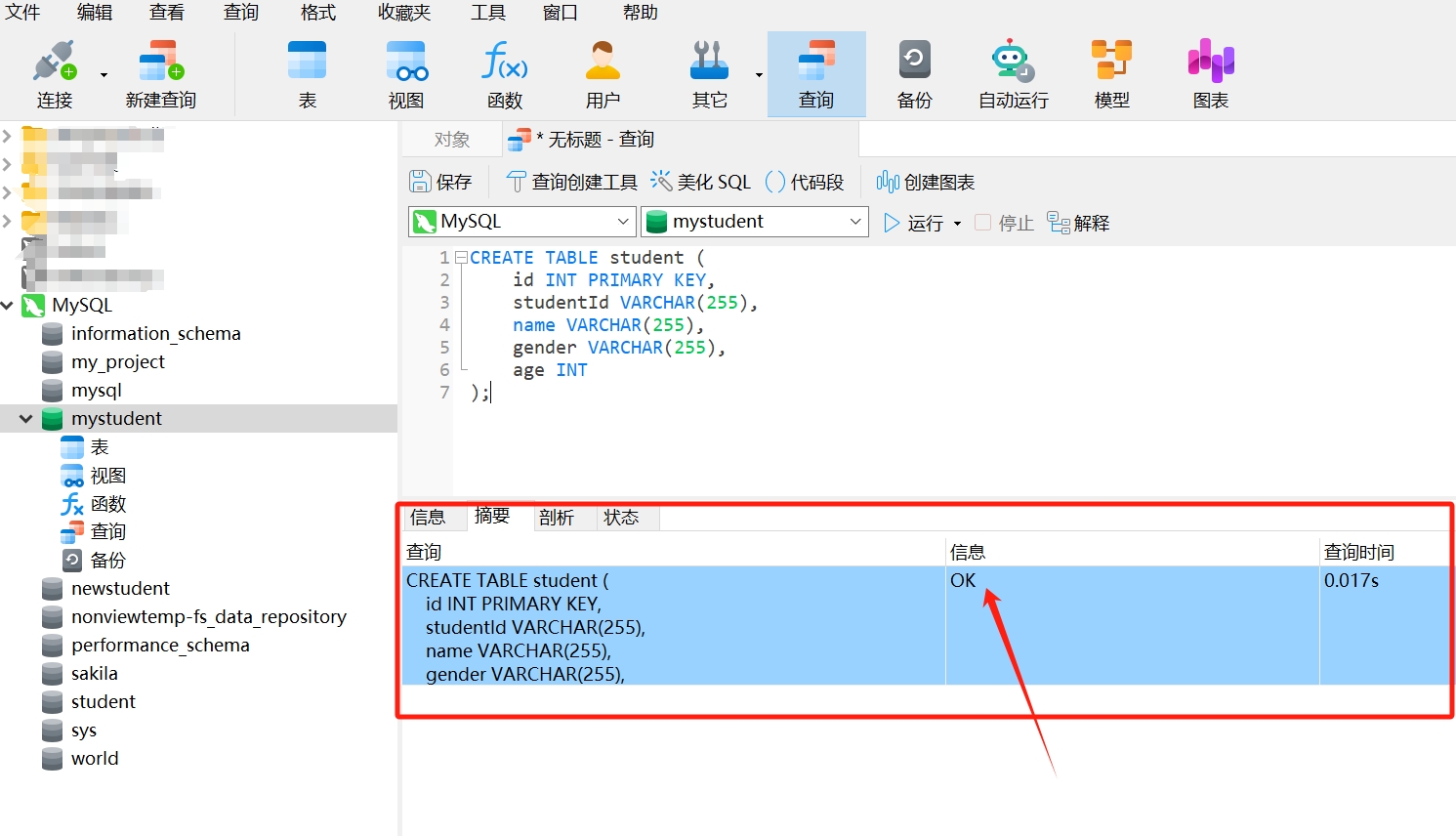
- Right-click and select "Refresh."
- After refreshing, double-click "Tables," and you will see the created data table "student" displayed in the "mystudent" database. Double-click "student" to open the data table. The style of the "student" table is as follows:
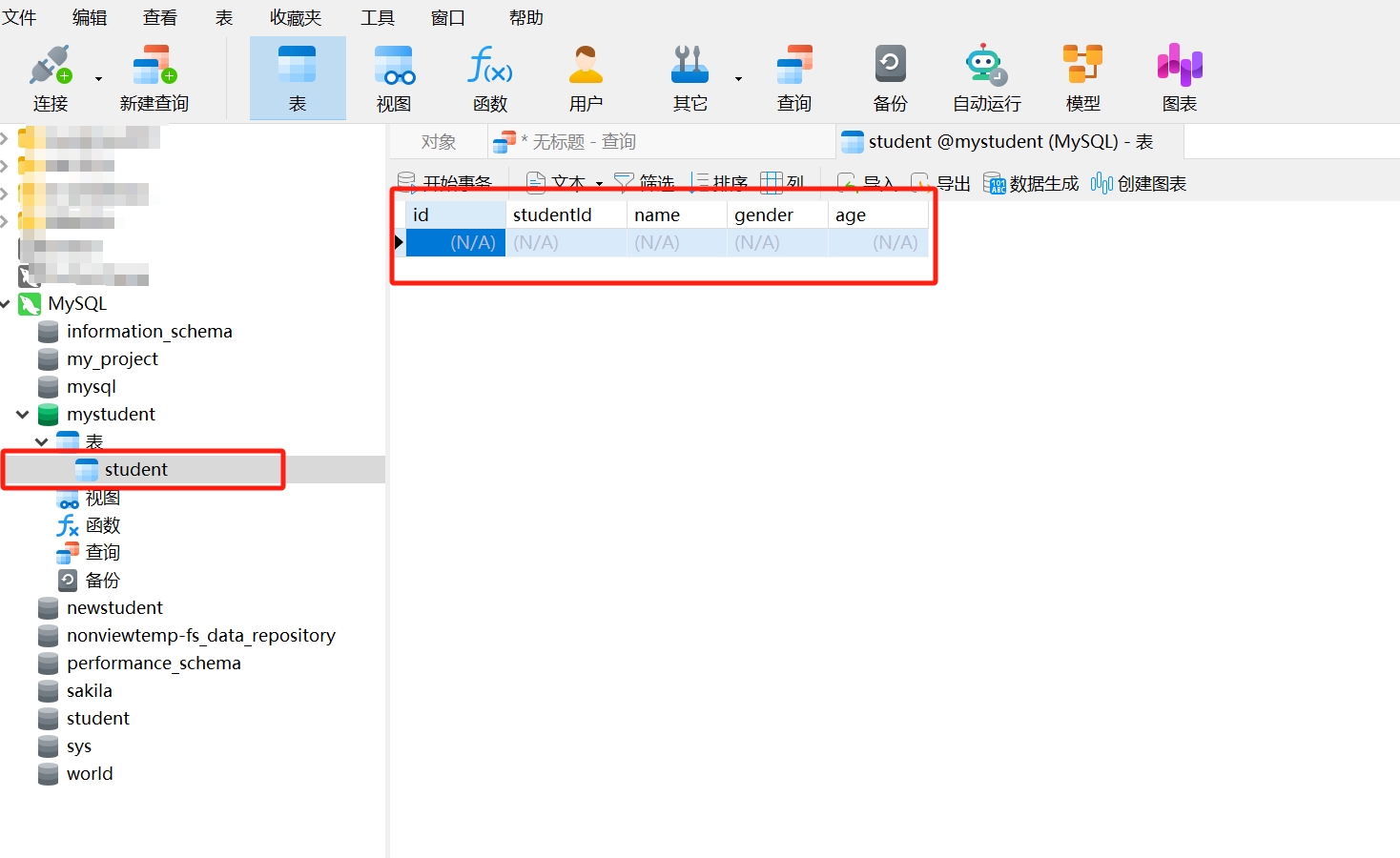
Thus, a data table has been created. Next, we will explain the definition of a data table through the "student" table.
Definition of a Data Table
Creating a new data table is the process of defining the structure and attributes of the data table. The definition of a data table includes the table name, column names, and data types of the columns, among other information. The table name is the unique identifier of the data table, used to distinguish different tables within the database; column names represent the attributes of the data, and each column has a name and data type that define the type of data stored in that column; the data type of the column defines the type of data stored in that column, such as integer, string, date, etc.
The SQL statement we used to create the data table earlier is an example of a data table definition:
CREATE TABLE student (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
studentId VARCHAR(255),
name VARCHAR(255),
gender VARCHAR(255),
age INT
);By creating the data table "student" using the SQL statement, we can clearly understand the appearance of the data table, as well as the structure of the data table and the meaning of each field. Our explanation of this example is as follows:
Table Name: The table name is the unique identifier of the data table, used to distinguish different tables within the database. In the above example, the table name is "student."
Fields: Fields are the attributes of the table. Each field has a name and data type, used to define the content that can be stored in that field. In the example, the fields include id, studentId, name, age, and gender.
Data Types: Data types define the type of data that can be stored in each field. In the example, there are integer types (INT) and character types (VARCHAR).
Primary Key: The primary key is a column or a group of columns in the table whose values can uniquely identify each row in the table. The existence of a primary key ensures that each record in the table is unique. In the example, the id column is designated as the primary key.
Example: Creating Data Tables student and sc in MyStudent
We have understood the definition of data tables, but the previously created data table only has a structure without actual data. Now, let’s run the following SQL statements in the SQL editor of Navicat to create complete data tables "student" and "sc" for further study:
- student Data Table (Basic Information Table for Students):
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`SId` varchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`Sname` varchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`Sage` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`Ssex` varchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('01', 'Zhao Lei', '1990-01-01 00:00:00', 'Male');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('02', 'Qian Dian', '1990-12-21 00:00:00', 'Male');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('03', 'Sun Feng', '1990-05-20 00:00:00', 'Male');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('04', 'Li Yun', '1990-08-06 00:00:00', 'Male');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('05', 'Zhou Mei', '1991-12-01 00:00:00', 'Female');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('06', 'Wu Lan', '1992-03-01 00:00:00', 'Female');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('07', 'Zheng Zhu', '1989-07-01 00:00:00', 'Female');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('09', 'Zhang Lan', '2017-12-20 00:00:00', 'Female');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('10', 'Li Hua', '2017-12-25 00:00:00', 'Female');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('11', 'Li Lan', '2017-12-30 00:00:00', 'Female');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('12', 'Zhao Hua', '2017-01-01 00:00:00', 'Female');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('13', 'Sun Mei', '2018-01-01 00:00:00', 'Female');- sc Data Table (Student Grades Table):
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `sc`;
CREATE TABLE `sc` (
`SId` varchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`Sname` varchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`Cname` varchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`score` decimal(18, 1) NULL DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('01','Zhao Lei', 'Chinese', 80.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('01','Zhao Lei', 'Mathematics', 90.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('01','Zhao Lei', 'English', 99.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('02','Zhao Lei', 'Chinese', 70.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('02','Qian Dian', 'Mathematics', 60.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('02','Qian Dian', 'English', 80.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('03','Sun Feng', 'Chinese', 80.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('03','Sun Feng', 'Mathematics', 80.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('03','Sun Feng', 'English', 80.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('04','Li Yun', 'Chinese', 50.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('04','Li Yun', 'Mathematics', 30.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('04','Li Yun', 'English', 20.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('05','Zhou Mei', 'Chinese', 76.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('05','Zhou Mei', 'Mathematics', 87.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('06','Wu Lan', 'Chinese', 31.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('06','Wu Lan', 'English', 34.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('07','Zheng Zhu', 'Mathematics', 89.0);
INSERT INTO `sc` VALUES ('07','Zheng Zhu', 'English', 98.0);3. Basic SQL Query Statements
Programming is about solving problems related to data insertion, deletion, modification, and querying. In relational databases, the basic operations for data management include adding, modifying, deleting, and querying, with querying being the most commonly used operation. The SELECT statement in SQL is used to retrieve data from the database, allowing you to choose which fields to retrieve from which table.
The basic syntax structure of the query statement SELECT is as follows:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name;Where SELECT is followed by the column names to be queried, which can be a single column or multiple columns separated by commas; FROM specifies the name of the data table to be queried.
Using SELECT Statement to Query Student Information
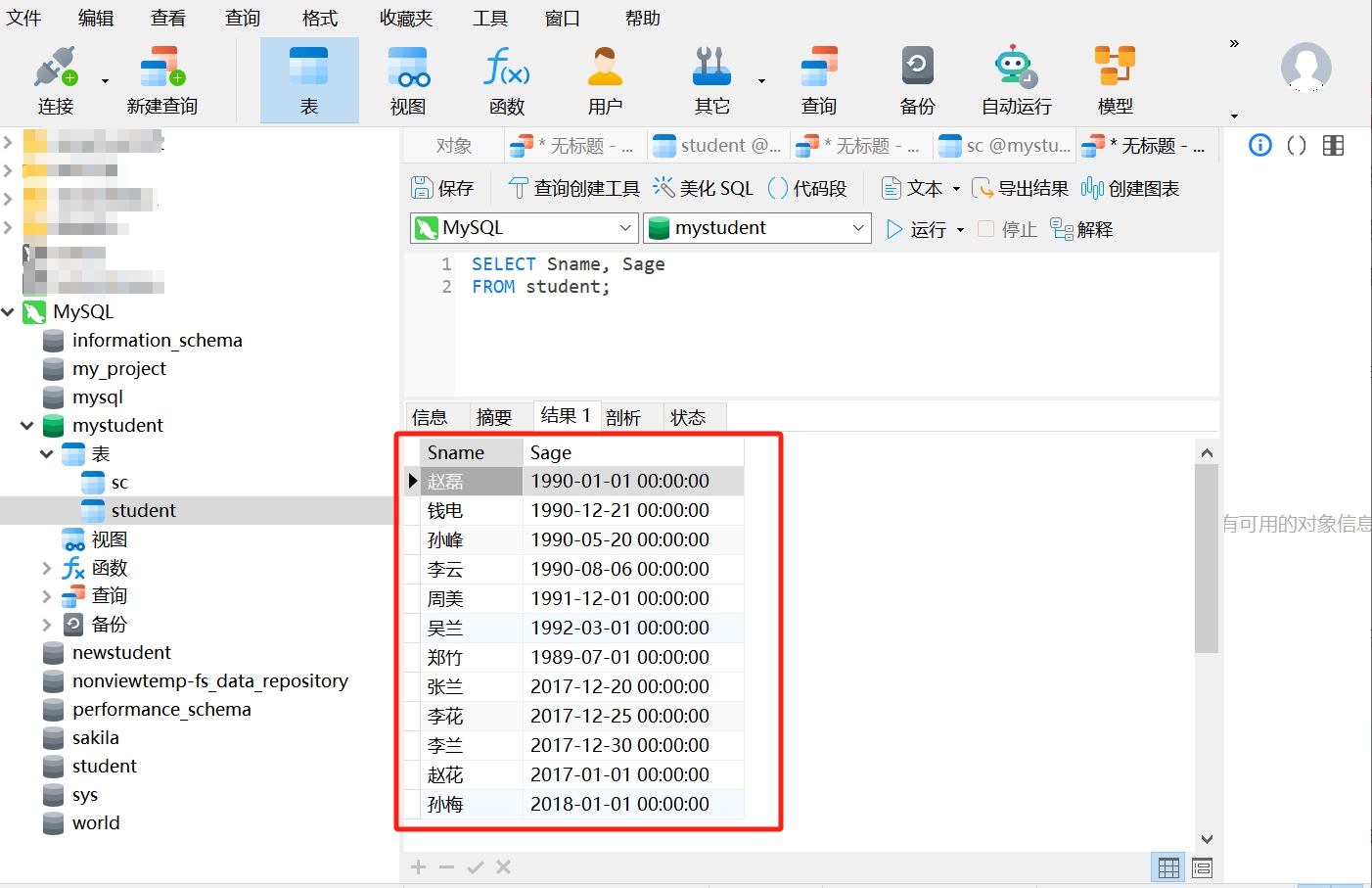
Now, we have a data table "student" that contains the columns SId, Sname, Sage, and Ssex. We can use the SELECT query statement to retrieve the names and birth dates of all students:
SELECT Sname, Sage
FROM student;When you run this query statement in Navicat, you will retrieve the names and birth dates of all students in the student table:
If you want to query all information from the student table, you can use the wildcard asterisk “ * ” to indicate “all”:
SELECT *
FROM student;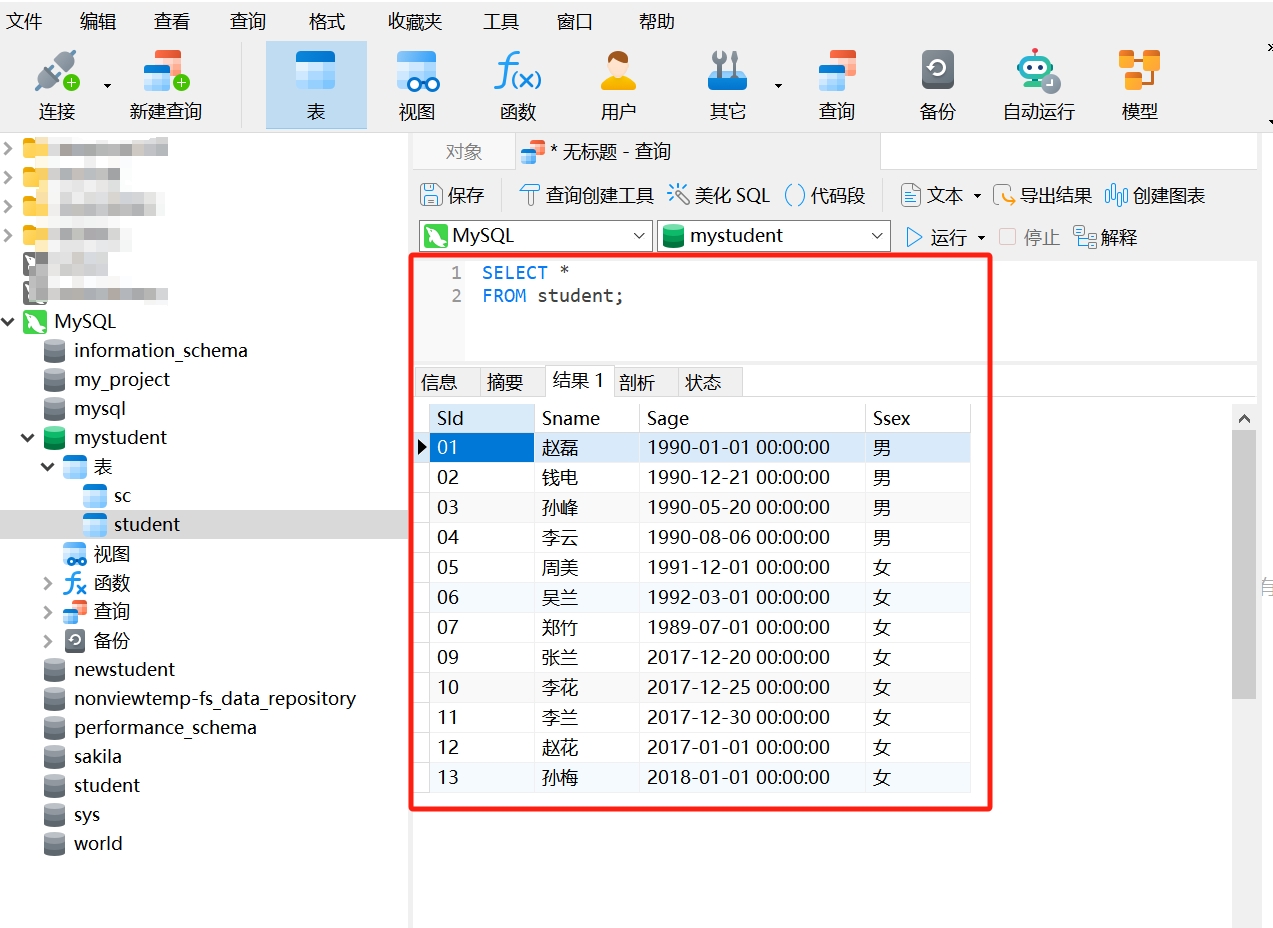
Using SELECT Statement to Query Student Grades
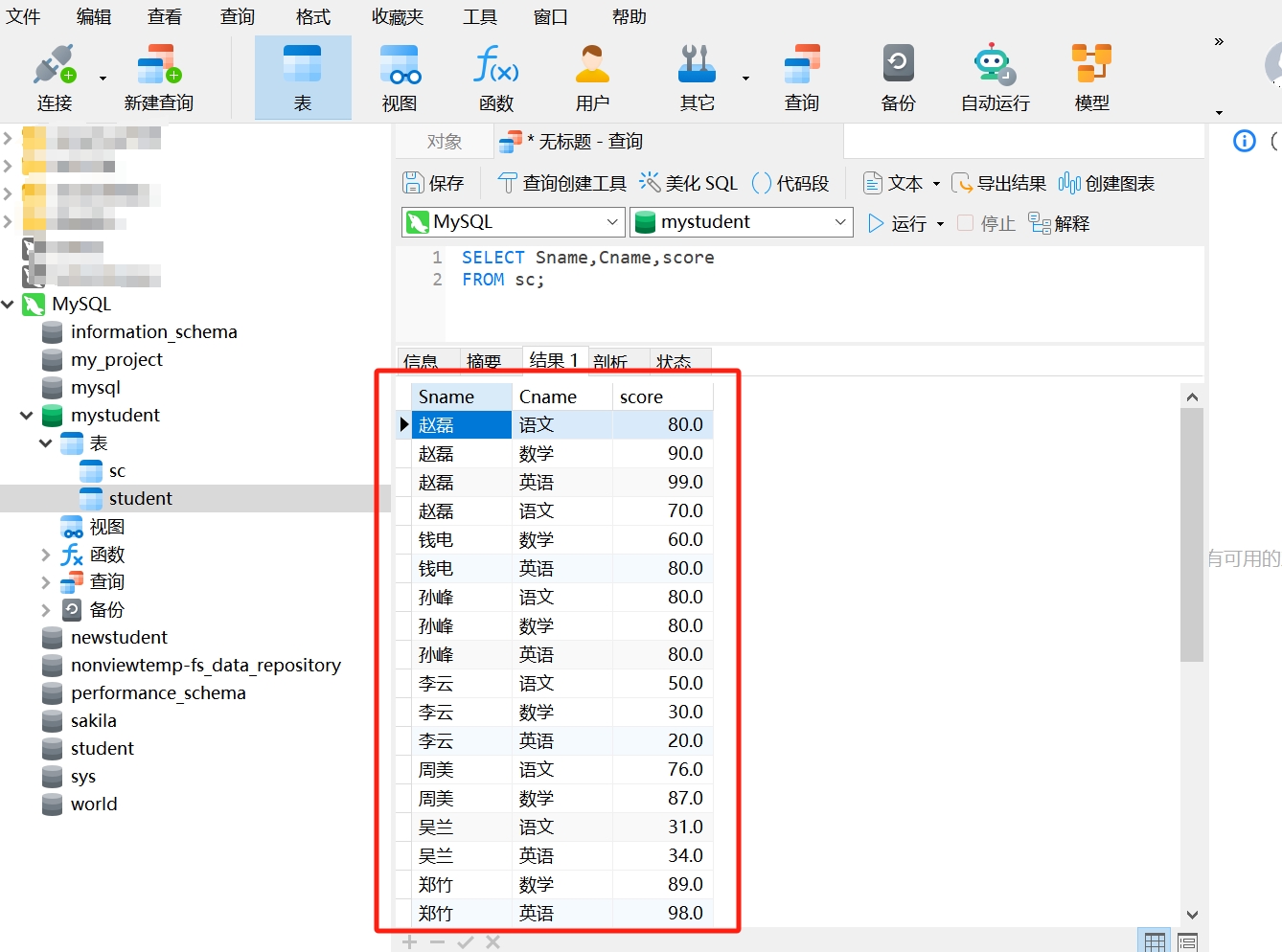
We can also query student grades. The data table "sc" contains the columns SId, Sname, Cname, and score. If we want to query all students' exam subjects and scores, we can also use the SELECT query statement:
SELECT Sname, Cname, score
FROM sc;When you run this query statement in Navicat, you will retrieve the exam subjects and scores of all students in the sc table:
4. Online Learning Resources
SQL Demonstration: Click here to download the demonstration code for this lesson.
Navicat Documentation Tutorial: https://www.openjianghu.org/doc/page/article/11866
SQL Tutorial: https://www.runoob.com/sql/sql-intro.html
MySQL Tutorial: https://www.runoob.com/mysql/mysql-tutorial.html
Liao Xuefeng's SQL Tutorial, with online practice: https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1177760294764384
5. Homework
Read the SQL documentation and quickly skim through it.
Download the SQL demonstration code for this lesson from the resources and create the four tables through new queries.
In Navicat, try more operations with the "Connect," "New Query," "Table," and other buttons, using SQL statements to practice creating databases and data tables, and querying student data.
